Dear Reader,
When I first read Mary Poppins and Mary Poppins Comes Back (which were printed in one volume) as a child, I was not able to enjoy the original illustrations by Mary Shepard, as they were not included in the Bulgarian translation published in 1980. Instead, they were replaced by illustrations by Lyuben Dimanov.

I don’t think I liked Dimanov’s illustrations as a child because I have no memory of them, and I do remember a lot of the illustrations from my childhood books. All I remember is that the book was very thick, and it felt like proof that I was really good at reading. It was only a couple of years ago when I retrieved an old copy of my childhood edition of Mary Poppins that I realized the original illustrations were not in it.
Now that I am acquainted with the original illustrations, I find it difficult to enjoy Dimanov’s interpretations of the characters. For one, I find the figures a bit too angular, and their proportions too exaggerated. Moreover, in my opinion, he took his artistic liberties to the extreme. In fact, one has to wonder if he even read the stories, or how he could portray Mary Poppins with long, curly, flowing hair like a lion’s mane.

I’m certain P.L. Travers would have been upset if she had seen these illustrations—or maybe she did. I wish I could show them to her and ask her opinion. What we do know is that she was very particular about how Mary Poppins was depicted and insisted on her being represented exactly as she had imagined her.
In fact, P.L. Travers was so particular about the character, and Mary Shepard was such an inexperienced artist at the start of the project, that the emergence of Mary Poppins in visual form was not without its growing pains.
P.L. Travers wanted Mary Poppins to be plain, yet graceful, and to help the young visual artist grasp her vision of the character, they took many walks in the park to observe nannies pushing prams. Yet despite Shepard’s heartfelt efforts, P.L. Travers was not satisfied with the sketches and it wasn’t until she found a wooden doll with bright black hair, bright blue eyes, and a turned-up nose, and showed it to Shepard, that Mary Poppins finally took shape.
The working relationship between P.L. Travers and Mary Shepard spanned over 50 years, during which Shepard illustrated all the Mary Poppins books, including the Latin translation of Mary Poppins, a children’s cookbook, an alphabet book, and a coloring book published in 1969. I had been searching online for this coloring book for a long time, and then, one day, I was fortunate enough to find an unused copy on Facebook Marketplace of all places.

Oh, the joy of finding it and coloring the illustrations! Of course, I kept the original coloring book pristine and worked on photocopied pages, in case anyone is curious. I want to keep it as a collectible, but I also love the idea of having the chance to color the illustrations again whenever the mood strikes. The time I spent coloring reminded me of how much I loved it as a child. It also reminded me of my struggles of not crossing over the lines—though, as it turns out, I still struggle with that! But perfection isn’t the point. The point is enjoyment and playfulness at any age!
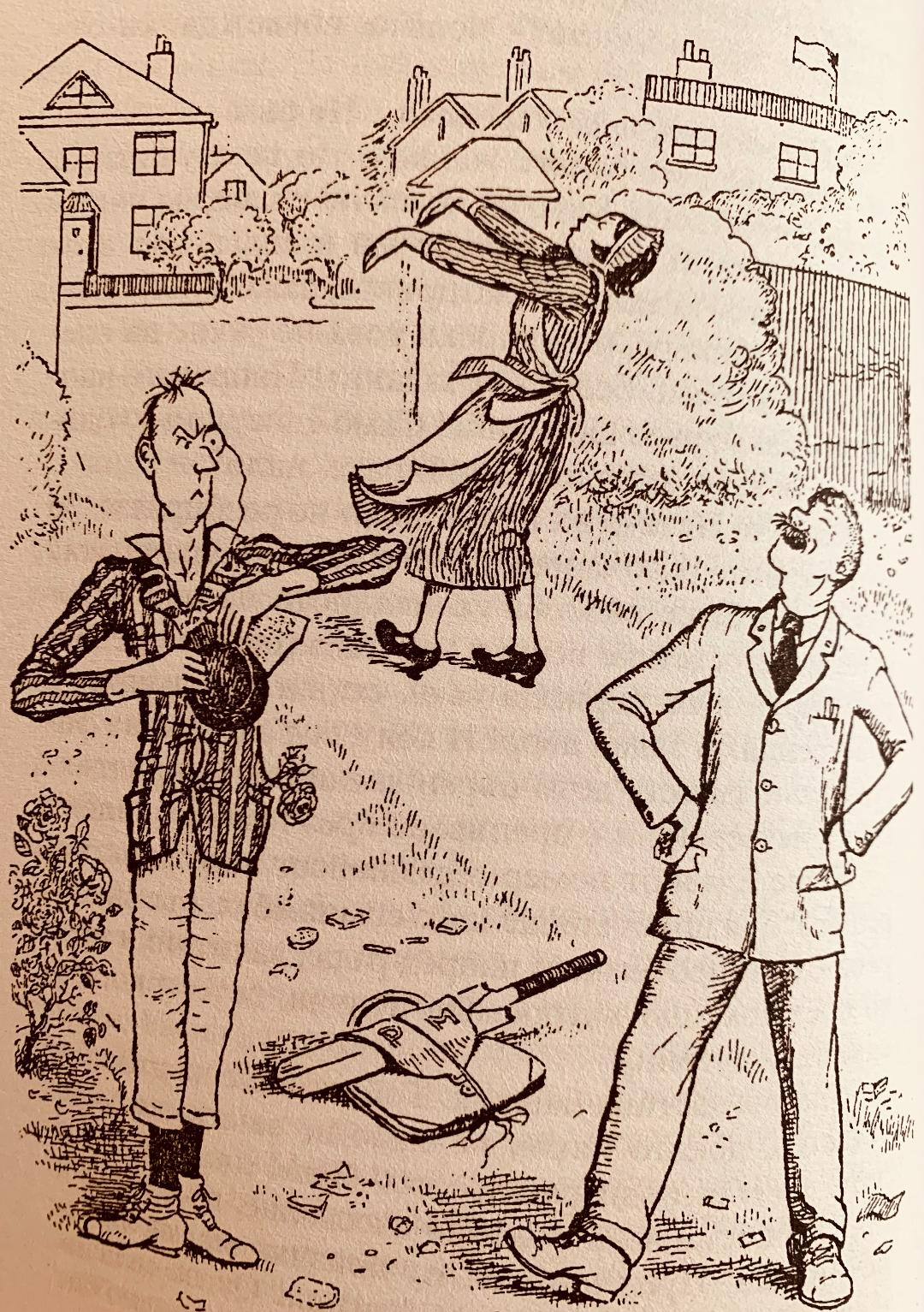
While coloring the pictures, I suddenly noticed something interesting in one of the illustrations that struck me as quite indicative of the nature of the relationship between Mary Shepard and P.L. Travers. Reportedly their relationship was a difficult one, P.L. Travers being portrayed as domineering and Mary Shepard as an underestimated, self-effacing artist. I believe that a glimpse of their relationship dynamic is reflected in one of the illustrations in the story “Balloons and Balloons”. This story first appears in the second book Mary Poppins Comes Back first published in 1935. Below is a picture of the illustration from the book.

The picture shows several of the Mary Poppins characters holding balloons with their names on them, floating through the air, with Mary Poppins as the central figure holding the largest balloon. But if you look up closely you will notice the two intruders in this picture. In the bottom left corner, you can see P.L. Travers and Mary Shepard joining the party. According to P.L. Travers, as she once told an interviewer, it was Mary Shepard’s idea to include them both in the illustration. (Personally, I think this was a genius idea.)
Notice how, in this picture, the two women are facing each other. Mary Shepard’s figure is slightly smaller, and her body curves in a way that seems to mold to the shape of P.L. Travers’ figure. Now, look at the picture below from the 1969 coloring book, keeping in mind that at the time, Shepard was bitter about not receiving any money from Disney for the movie adaptation of the character.

The figures are notably different in size and body language. P.L. Travers is larger and holds a bigger balloon. Her body flows gracefully through the air, with the string of her balloon twirling as she holds it effortlessly, without any strain. On the other hand, Mary Shepard, much smaller, is holding onto a short, tight string and appears tense, as if hanging on for dear life. Not only that, but she has her back turned to P.L. Travers.
I wonder if P.L. Travers noticed these changes in their positioning in the illustration, or if this detail completely escaped her, or if she would have even cared about it. I haven’t had the chance to delve deeper into their relationship, so I’m relying on what others have written about the subject and while I’m aware that I’m speculating on the comparative interpretation of these two illustrations, it was, nevertheless, a fun insight to gain from my interaction with A Mary Poppins Story for Coloring.
As for P.L. Travers’s view that ‘what counts most is the text, not the picture,’ I both agree and disagree with her. It all depends on the angle from which you look at the question. Of course, there would be no picture of Mary Poppins without the story, but for children, the illustrations are almost as important as the text.
Perhaps it’s because P.L. Travers never intended the books to be read solely by children that she prioritized the text. Or, maybe it was because she was human and fallible, and possessive of Mary Poppins. After all, she once told an interviewer that a fictional character is like a child to an author. One thing is certain: despite their differences, both P.L. Travers and Mary Shepard must have both gained something positive from their collaboration. Otherwise, why continue for fifty years?
I hope you enjoyed reading this blog post and that you’ll subscribe to my blog, so you don’t miss the next installment. While I can’t commit to a regular posting schedule, one thing I can promise is that I’ll continue writing about all things Mary Poppins and P.L. Travers.