Dear Reader,
This blog post is going to be slightly more personal than usual as I want to share with you one of the many Mary Poppins effects in my personal life. These, for me magical, effects are incontestably transformative and have greatly enriched my inner life and personal happiness. That said, I am not suggesting that all personal challenges have vanished, but my ability to sustain and show resilience comes directly from these various effects.
First and foremost, reconnecting with my childhood reading of “Mary Poppins” reminded me of my deep love for magic and fairy tales. It also made me realize that my daily life had, sadly, become quite dull and ordinary. It’s not that I wasn’t surrounded by people and events—my life was filled with all the things that keep us busy and distracted. Of course, my family is a great source of love and support, and I am forever grateful to them, but there was an emptiness within me that couldn’t be filled by anyone, no matter how loving they were. It just dawned on me (and perhaps this realization had been building up inside of me for some time) that I felt constrained. Faced with this moment of recognition I had to acknowledge the need for more joy and wonder in my life.
But where to find them?
I decided to go search for them in the places where I had found them as a child. The day had come when I was finally old enough to start reading fairy tales again, to paraphrase a quote by C.S. Lewis. I felt goosebumps when I first read this quote by C.S. Lewis because the truth of his words resonated so deeply with my own experience.
Then, organically, one thing led to another, and I found myself collecting old books of fairy tales and fantastical adventures, something that I would never have thought I would be doing a few years ago, as it was so remote from the spheres in which I operated.
The moments I spend reading fairy tales and fantasy novels, or treasure hunting for old books, are pure bliss—a breath of fresh air in my daily life. It’s not just an escape from the ordinary; these activities also allow me to see the world in a new light. Looking at my bookshelves fills me not only with joy but with a sense of groundedness—a feeling of coming home. And I owe it all to P.L. Travers and her Mary Poppins.
Here, I’m sharing some pictures of the books in my modest collection, which I hope will expand over time.
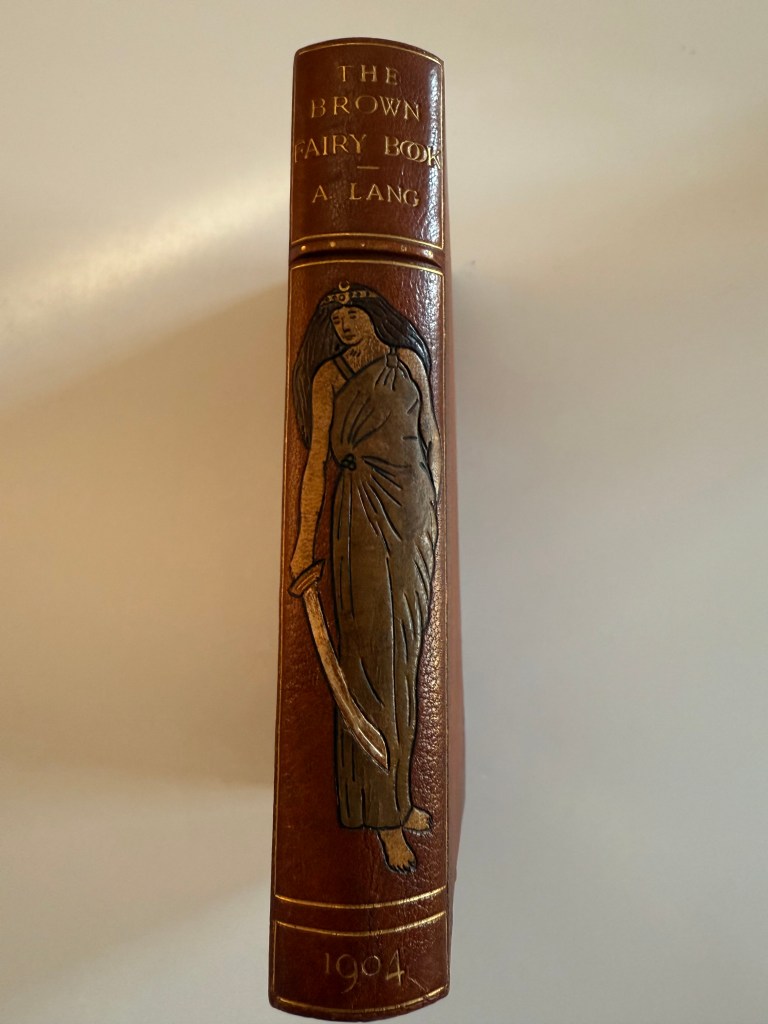


The Brown Fairy Book by Andrew Lang. Illustration below is by H.J. Ford.

Below is a picture of the cover of Princes and Princesses by Andrew Lang.

Illustration below by H.J. Ford.

Below is the cover of Myths & Legends of Japan by F. Hadland Davis.

Illustration below by Evelyn Paul.



While reading interviews given by P.L. Travers, I discovered that our childhood readings intersected, despite our cultural and generational differences. We both read Beatrix Potter, the Brothers Grimm, and Andersen’s fairy tales, to name a few, only I read them translated in Bulgarian. This realization brought back memories of the fairy tales from my own childhood, with their beautiful illustrations, and I felt a deep grief for having left behind the most cherished treasure of all—my books.
My initial response to counter this grief was to dismiss it as childish. I told myself I had to accept certain losses in life. On a practical level, I also thought it unrealistic to expect I could find copies of these books now that I live so far from my birthplace. But was I being childish? Was this a loss that needed to be accepted, or was it the kind of loss that could be retrieved? P.L. Travers herself pondered the theme of loss often, and in her later years, she would say that all that is lost is somewhere.
I decided to give it a try, and with the help of the internet, I’m happy to report that, after a couple of years, I was able to reconstruct most of my childhood fairy tale book collection. I successfully found old copies of the editions I had as a child, as well as some new reprints of those same editions.
These were the books my mother read to me at bedtime and the ones I learned to read with, before I got acquainted with Mary Poppins.
Below are pictures of the illustrations in my copy of Sleeping Beauty. The illustrator is Italian artist Gianni Benvenuti. This was P.L. Travers’s favourite fairy tale. She even wrote her own retelling of it and I wrote two blog posts about it back in 2017; you can read one of them here, and if you’re interested, the other is easily found on the website of this blog.

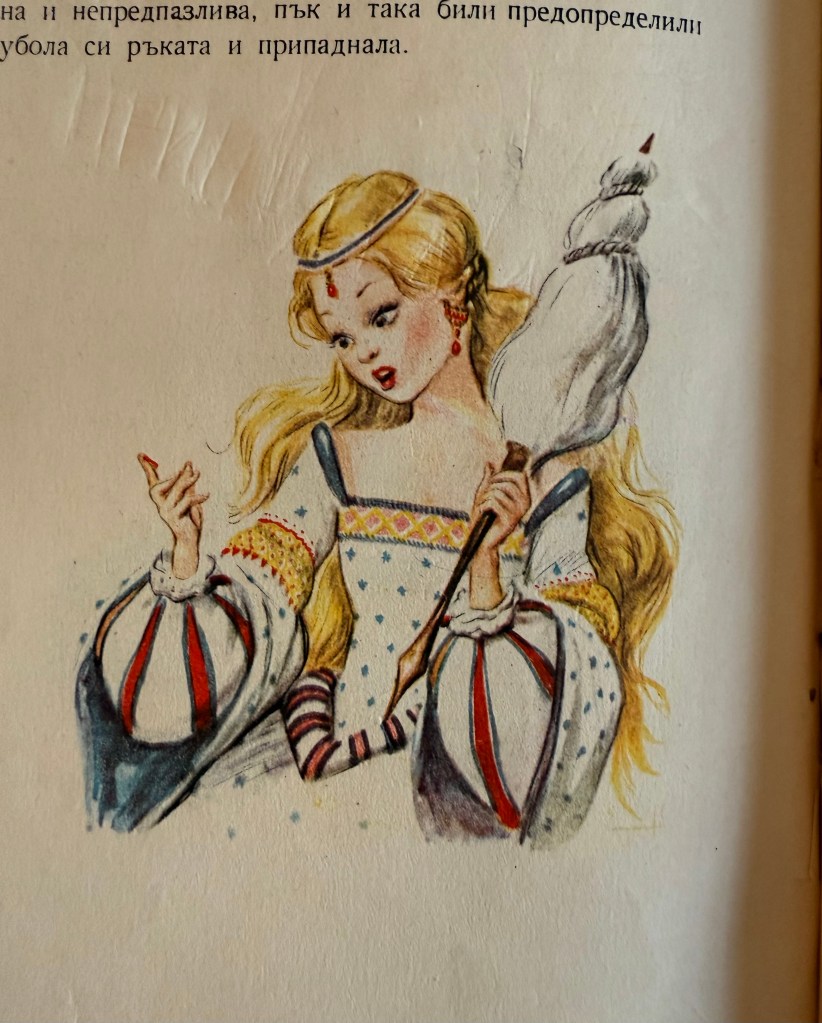

Cinderella was my personal favourite fairy tale as a child, followed closely by Snow White, mostly because Snow White had dark hair like mine. The illustrations below are also by Benvenuti.
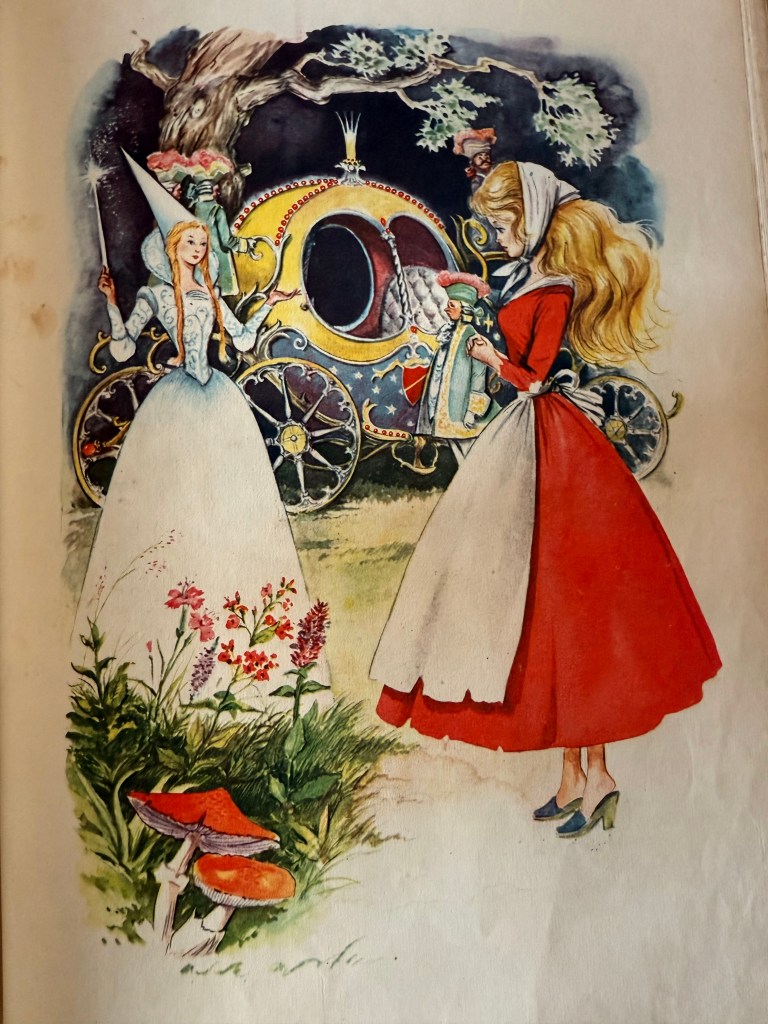
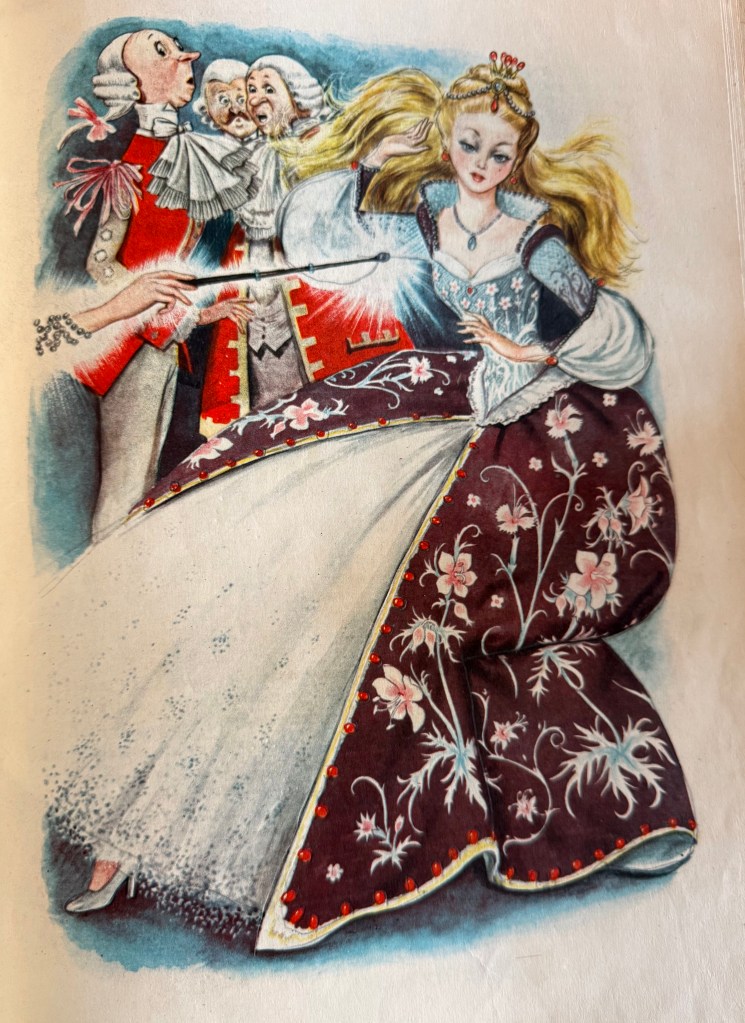



The illustrations of Snow White below are by Sandro Nardini.



And these are my two books of Andersen’s fairy tales. One is quite tattered, and the illustrations aren’t as beautiful as in the other, but I still enjoyed the stories. P.L. Travers loved Andersen’s fairy tales as a child, but as an adult, she had a different view. She believed Andersen undermined the vitality of his stories through his constant appeal for pity. It’s an interesting perspective, but one I don’t share.



The illustrations above are by Lyuben Zidarov. And the illustrations below are by Libico Maraja.



Here is now Peter Rabbit by Beatrix Potter. I must have been around three years old when my mother read Beatrix Potter’s stories to me, and I remember the illustrations captivated me with such magnetic force. I wish I had P.L. Travers’s lyrical talent to describe the experience. It’s hard to put emotional states and impressions into words, but it truly felt as if I was part of the picture. It’s a strange feeling to remember the state yet not be able to recreate the experience. I still enjoy the illustrations, but our perceptions do grow duller as we age.




P.L. Travers adored Beatrix Potter and wrote a review of The Tale of Beatrix Potter by Margaret Lane. I wrote a blog post about it some time ago, you can read it here.
This is all for now. I’ll share more of my childhood book collection in a future post. In the meantime, take care, and I hope you’ll return to read more about Mary Poppins, P.L. Travers, and my adventures as I continue to explore their world.